
Sexually transmitted infections are becoming very common. Here we review a list of STIs (also called STDs), the types of bacteria and viruses causing them, most common symptoms, and STD testing and treatment options.

An infection that spreads through sexual contact is called STI (sexually transmitted infection) or STD (sexually transmitted disease).
When one of the partners is already infected, an STI spreads to the other. And if they have multiple partners, STIs can spread to many people.
Over time, as the newly infected people have sexual relationships with others, the cycle of infection grows to more and more people.
That's why STDs are serious public health problem and affect millions of people.
If not tested in time and treated appropriately, they can cause lot of pain, trauma and even infertility and loss of pregnancy.
The causes of sexually transmitted infections are often bacteria or viruses.
Below we discuss a few common types of STIs, how they spread, the pathogens causing the infection, and recommendations to avoid them.

The graph above lists new and ongoing infections for most common sexually transmitted infections (2018). As you can see, HPV is by far the most common STI in US.
There are over twenty different STDs or STIs. Here we review a few of them from a long list of STDs.
Chlamydia
Gonorrhea
Syphilis
HPV (human papillomavirus)
Genital herpes
Trichomoniasis
Hepatitis B and C (Hep B, Hep C)
HIV / AIDS
Bacterial Vaginosis
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Monkeypox
Chancroid
Lymphogranuloma venereum
Mycoplasma genitalium
The "Clap" is a colloquial term for symptoms of common STIs, e.g., Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. The term comes from the "clapping" or "dripping" sound of peeing during a burning sensation.
The risk of each STI varies but Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis are some of the most commonly tracked by the public health authorities including CDC.

Chlamydia is one of the most common STI in teens and young adults that might not show any symptoms.
Chlamydia is caused by a bacterium chlamydia trachomatis.
Use of protection can prevent the spread but one should test as soon as possible to avoid serious risk to health. The CDC recommend that young women should regularly test for chlamydia.
Untreated infection can cause infertility and women might get pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
PID can cause pain around pelvis during sex or while peeing and bleeding during sex which can be heavy during menstrual cycle.
A discreet at home chlamydia test is an easy way to confirm the symptoms before starting a treatment.
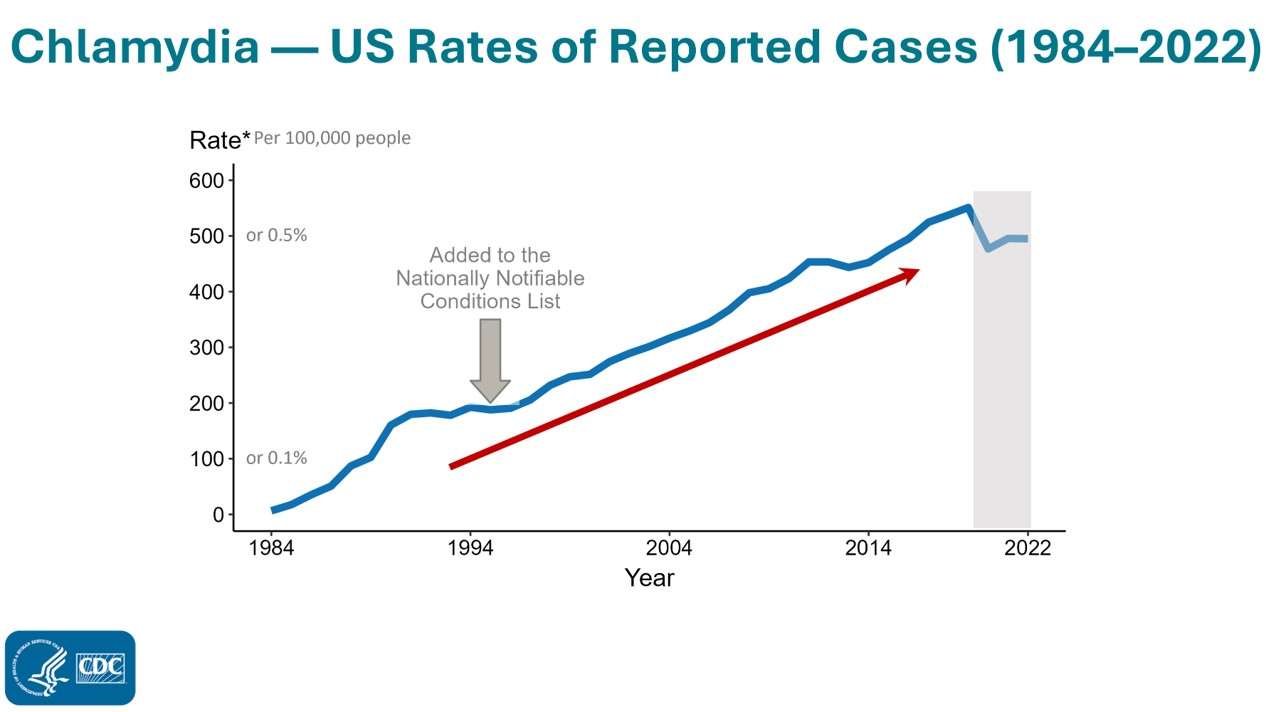
The number of chlamydia cases continue to rise.
Women are at much higher risk of chlamydia infections than men. This is especially true for young women and teenagers.
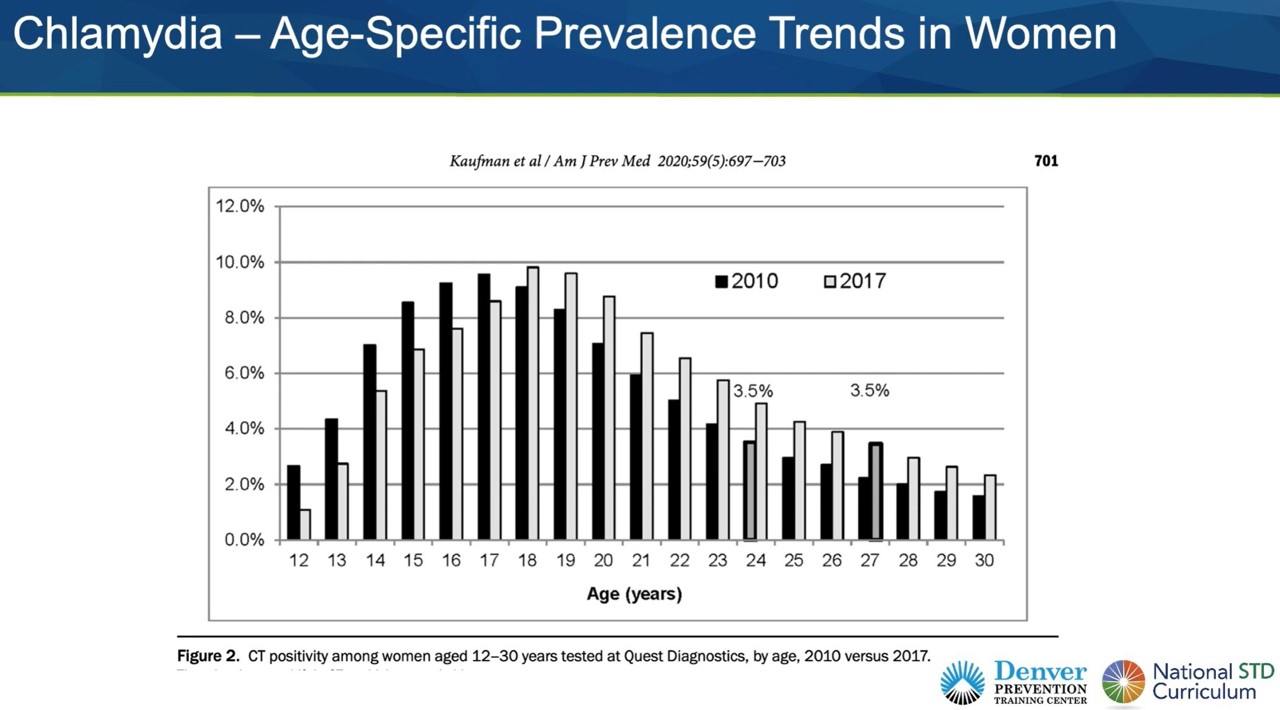
A plot comparing chlamydia infections among women (in 2010 vs 2017).
Young women have much higher rates of infection.
However, sexual education has shifted the peak age over the years but total cases still remain high.

Gonorrhea is very common STI caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
N. gonorrhoeae or "gonococcus", belongs to the family of bacteria that also cause meningitis & sepsis.
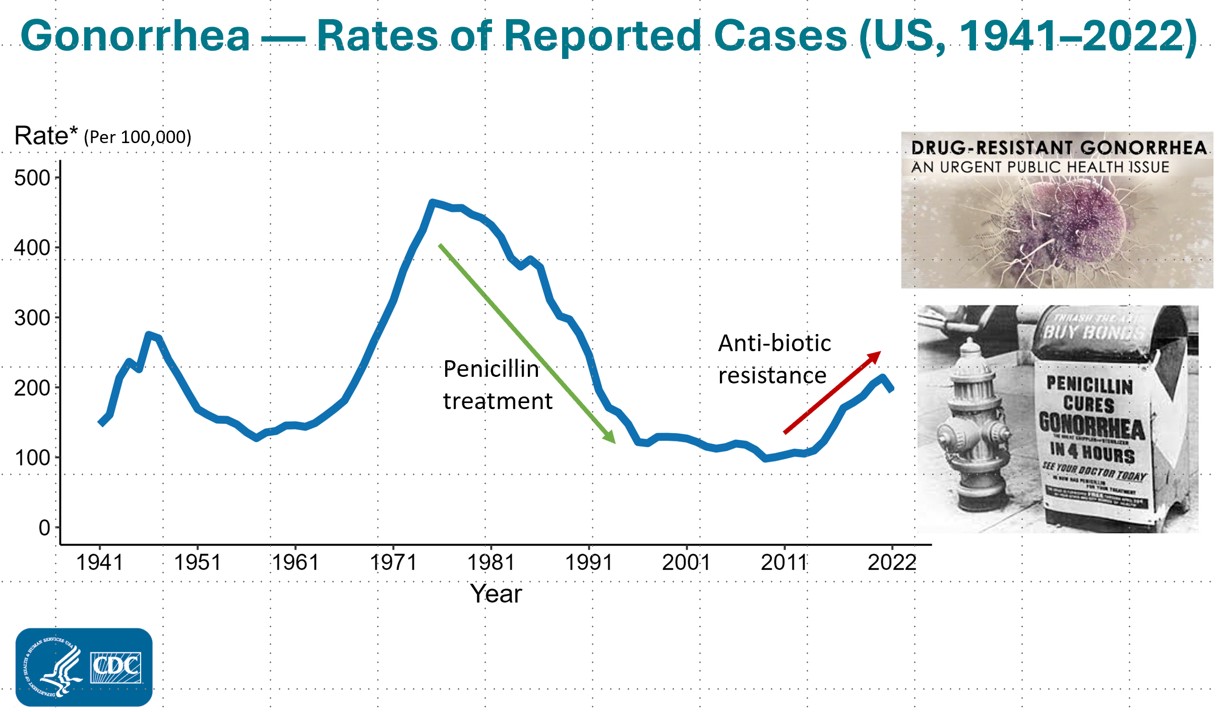
Rate of gonorrhea infection in US - the drop was due to very effective penicillin treatment but the bacteria soon developed resistance.
The symptoms might be mild or even delayed for a long time but are very similar to Chlamydia and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Gonorrhea often causes pain while urinating and puss-like discharge.
Men might observe pain in testicles and women might notice pain in their lower belly.
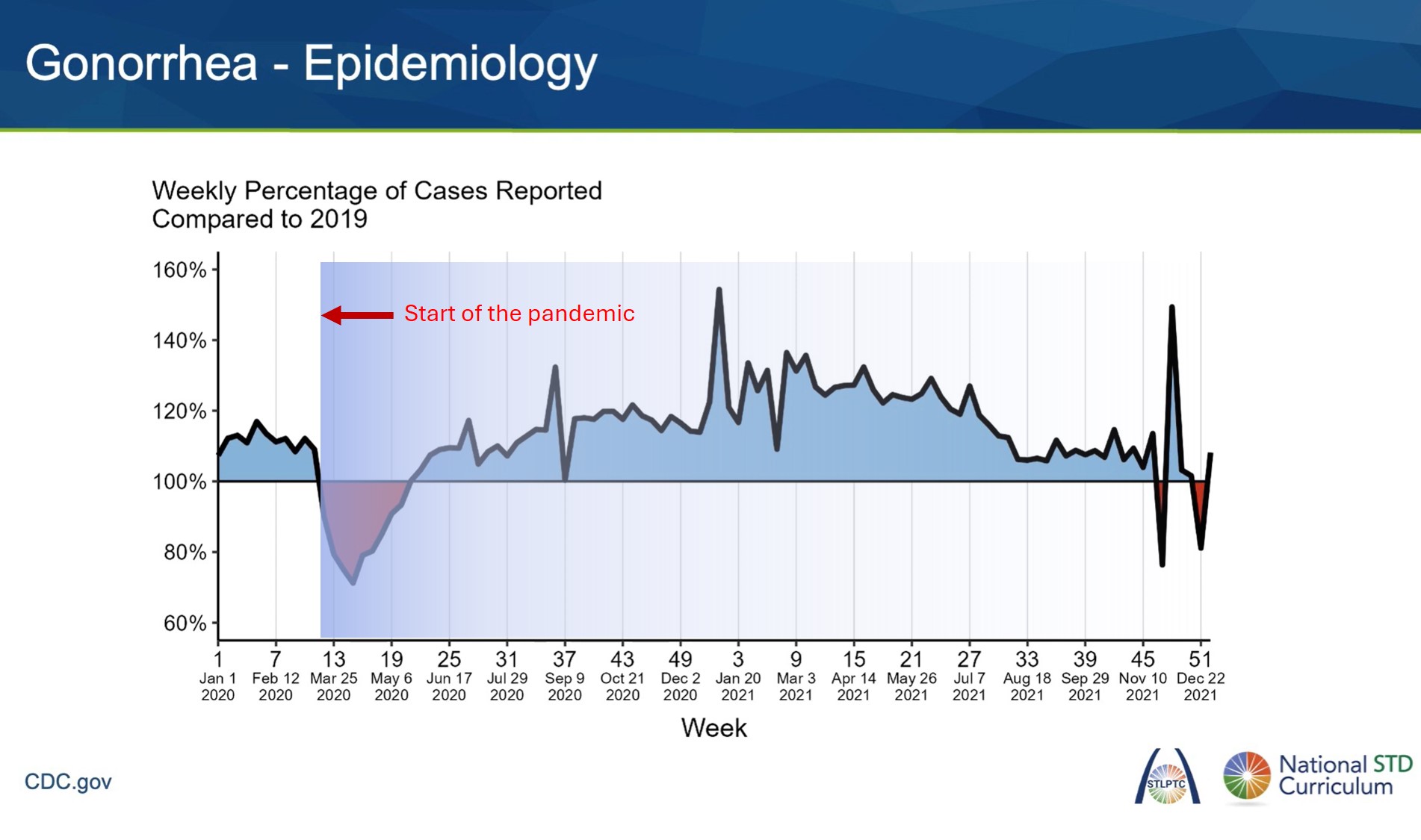
This chart shows the trend of gonorrhea infections stayed high during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Lots of STD clinics closed at this time but weekly reported cases stayed high despite the lockdown.
Why?
Because gonorrhea symptoms are very difficult to ignore (whenever they show up--although they are rare).
People visited emergency rooms (ER) to get treated, which kept the case count high.
The symptoms might be mild or even delayed for a long time but are very similar to Chlamydia and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Gonorrhea often causes pain while urinating and puss-like discharge.
Men might observe pain in testicles and women might notice pain in their lower belly.
It is recommended to use protection or test regularly whenever you have or your partner are sexually active outside your relationship.
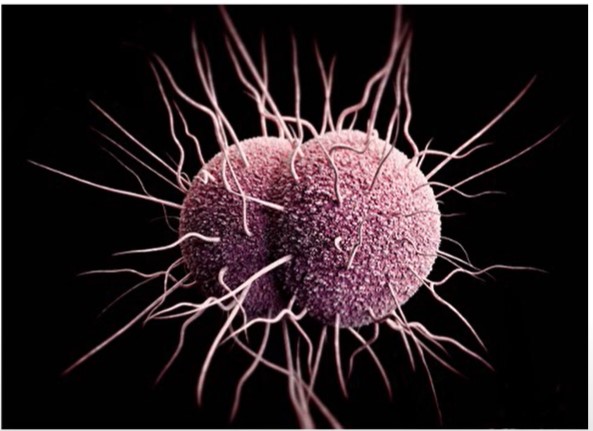
A microscope image of N gonorrhoeae. Credit: std.uw.edu
Neisseria are gram-negative bacteria that appear as double dots when seen on a microscope (see image above).
It has special affinity to mucous and binds to the outer (epithelial) cells of different organs.
It is very easy to get re-infected for gonorrhea because the bacteria have several ways to fight the immune system.
Gonorrhea rarely shows symptoms. But it is easy to treat after confirming with an at-home STD test.
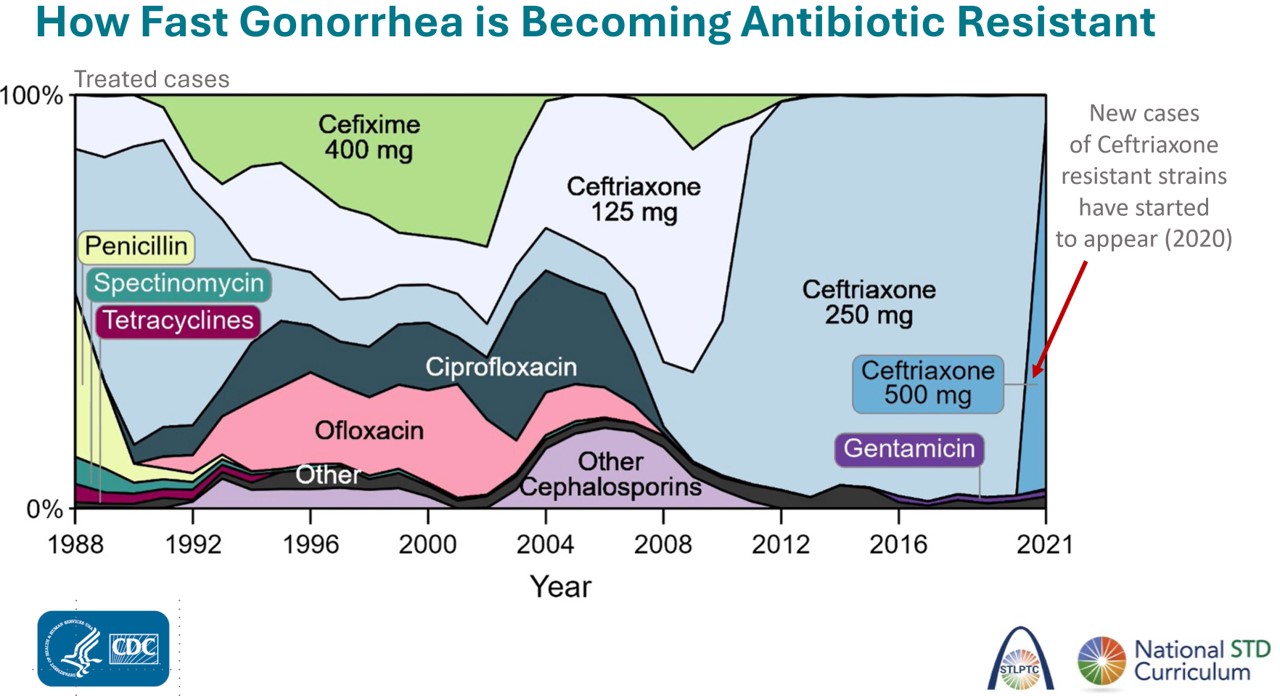
The figure above shows how quickly N. gonorrhoeae has developed resistance to antibiotics.
In fact, new cases are just starting to show up with resistance to Ceftriaxone, the latest antibiotic used to tread gonorrhea.

The STD syphilis is caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum.
The graph in the image above shows a five-fold increase in syphilis over past 20 years.
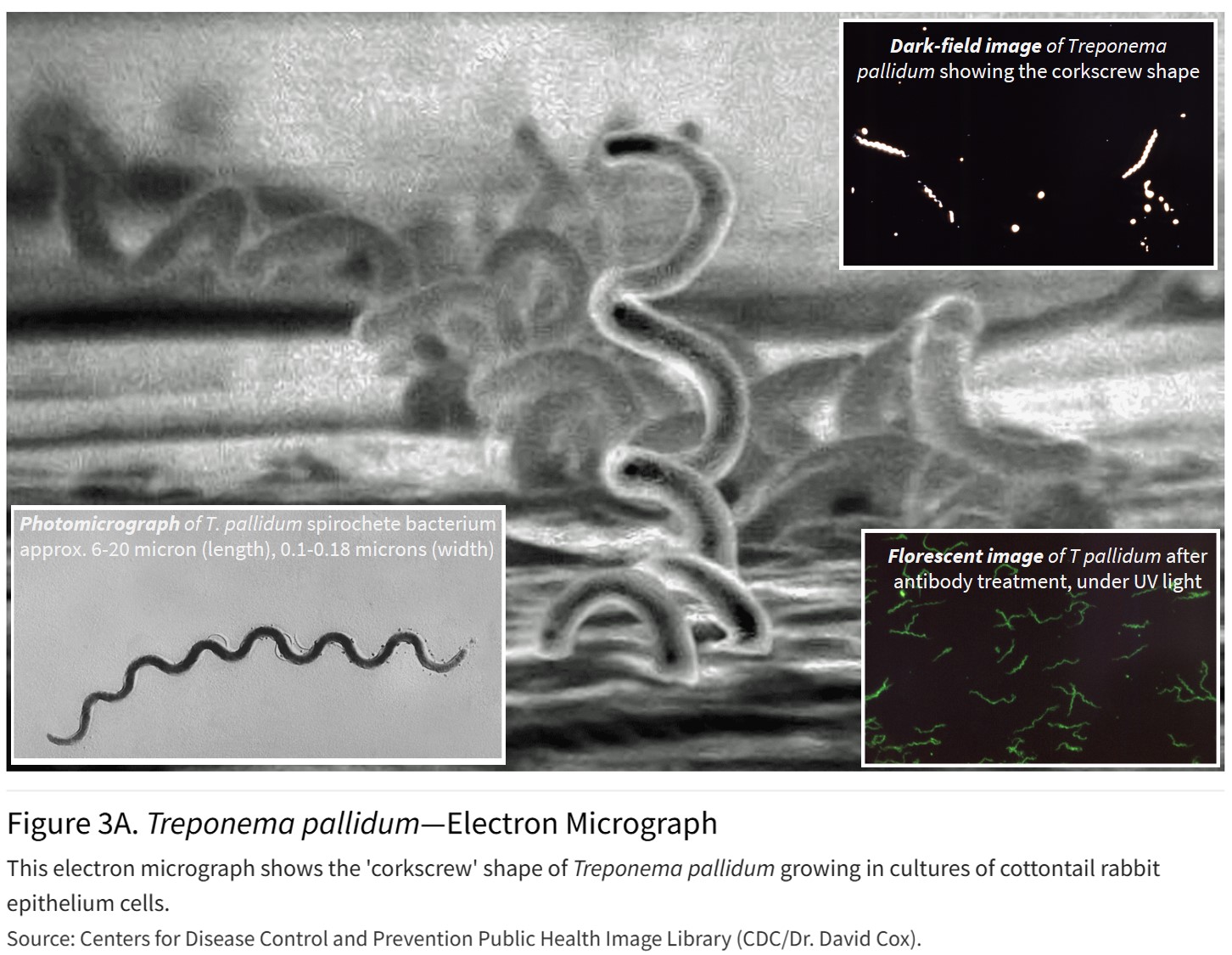
Syphilis is caused by corkscrew shaped bacteria called Treponema pallidum (meaning 'pale turning thread').
The thin (150 nm) but highly elongated (10s of microns) bacteria spread through skin & mucous abrasions during sexual contact.
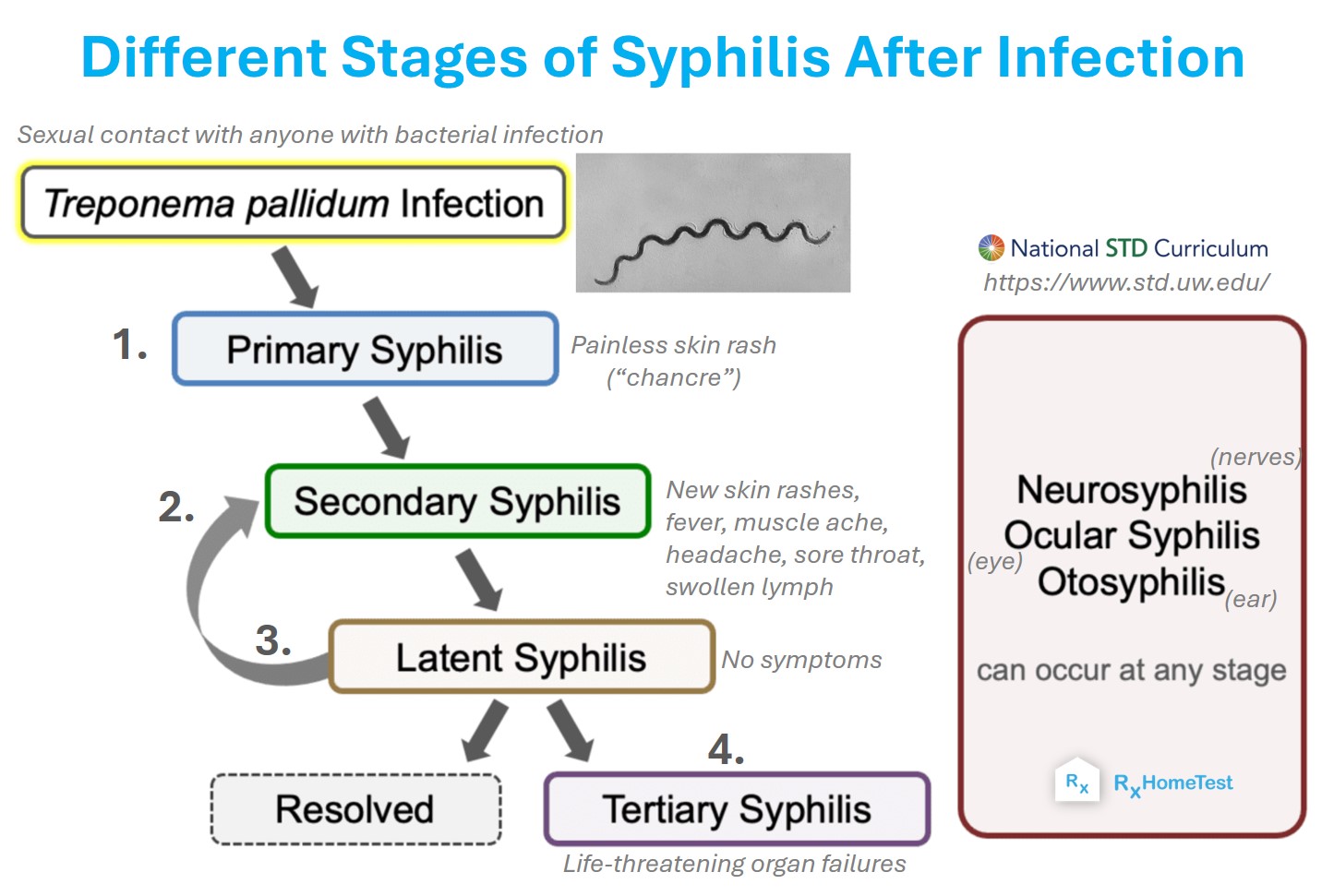
A graphical sketch of the four different stages of syphilis.
At first, painless sores and warts appear around the groin, genitals, and mouth for 2-3 weeks as the bacteria incubate.
As these disappear, the second stage involves rashes on palms of hands and soles of the feet lasting 2-4 weeks.
You may see other symptoms including mild fever, swollen glands, body ache, fatigue, sore throat, itching, loss of hair in random patches or weight loss.
The third stage is called latent stage without any symptoms for months or even years before returning as the final stage called tertiary syphilis.
This stage can lead to serious consequences including damage to heart, brain, liver, eyes, and joints. It can also transfer from mothers to babies.
Syphilis is called a 'great imitator' as symptoms resemble to many common health conditions (sores, fever, red skin, swelling).
Syphilis is easily treatable with antibiotics but requires testing to confirm an infection.
HPV is the most common STI worldwide. Almost 1 in 6 people is infected with HPV in the world at any given time.
But there is no way to confirm an HPV infection since symptoms are rare and people might not know they are infected.

Some people may observe genital warts and women might see abnormal precancerous cells on the cervix.
HPV is not a single virus, but a group that can be tested in women with a vaginal swab before it can lead to cervical cancer.
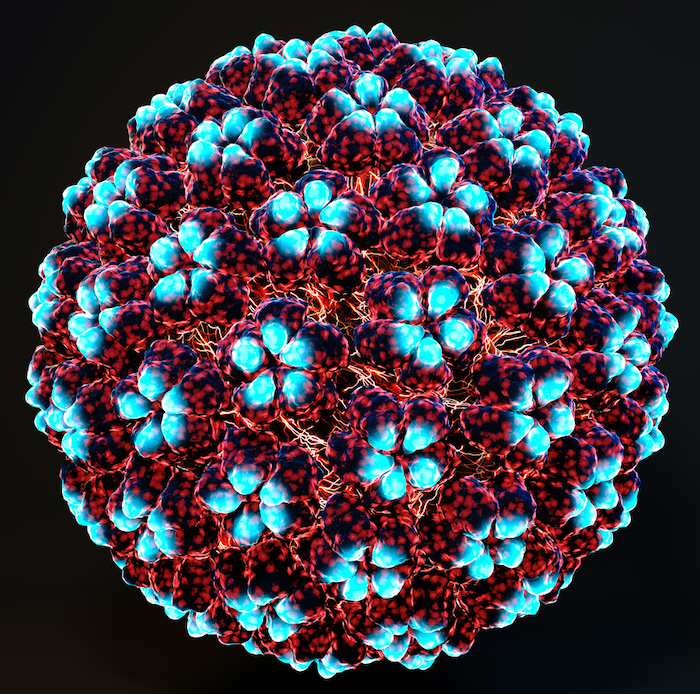
An computer enhanced image of the HPV virus. Credit: std.uw.edu
Human papillomavirus has 40 different varieties:
The low-risk types (6, 11) cause 90% of groin warts.
The high-risk types (16, 18) cause 70% of cervical cancers.
Types 31, 33, 45, 52, 58 cause another 10% of cervical cancers.
There is no cure for HPV, but an early STD testing and regular pep-smears can help detect any infections.
HPV vaccines are available today and recommended for those under the age of 26 years. They have been effective reducing HPV infections.

Genital herpes is an extremely common sexually transmitted infection but it is a relatively low risk STD.
In fact, the WHO says herpes simplex viruses (HSV) are everywhere.
As many as 7 in 10 people might be infected by HSV-1.
500 million people under the age of 50 years might be positive for HSV-2.
Herpes is caused by the Herpes simplex virus which causes sores and blisters on the mouth (called HSV-1) and genitals (HSV-2).
Normally, herpes sores heal in 2-4 weeks. But they may reappear four-five times in a year causing a herpes outbreak.
Flu-like symptoms of chills, fever, body pain are also common.
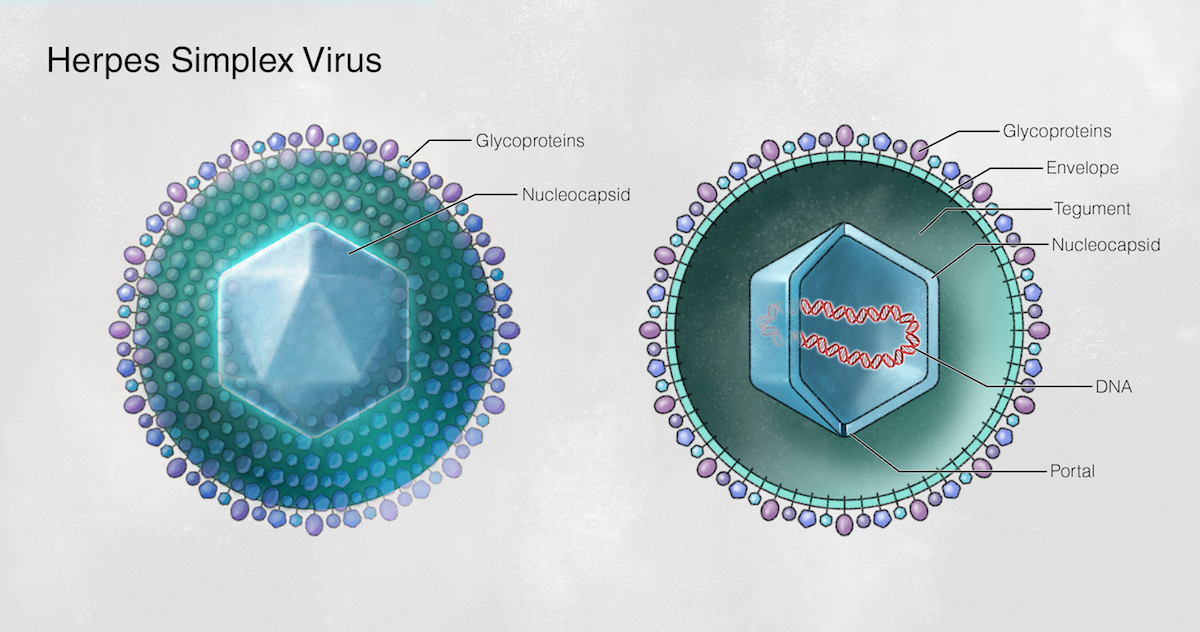
A sketch showing the basic structure of the herpes simplex virus with a double-stranded DNA.
There are 9 known herpesviruses that can cause several different kinds of infections:
Chickenpox
Shingles
Infectious mononucleosis
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Oral and genital herpes
In general, herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) can easily spread through skin contact and saliva.
HSV-1 infections (or oral herpes or cold sores) are more common.
However, HSV-2 causes genital herpes (leading to sores, blisters, etc.), an infection that may never be cured throughout the life of an infected person.
With a genital ulcer test, it's possible to differentiate between HSV1 and HSV2.
Herpes outbreaks can cause serious blisters and sometimes maybe as frequent as every month.
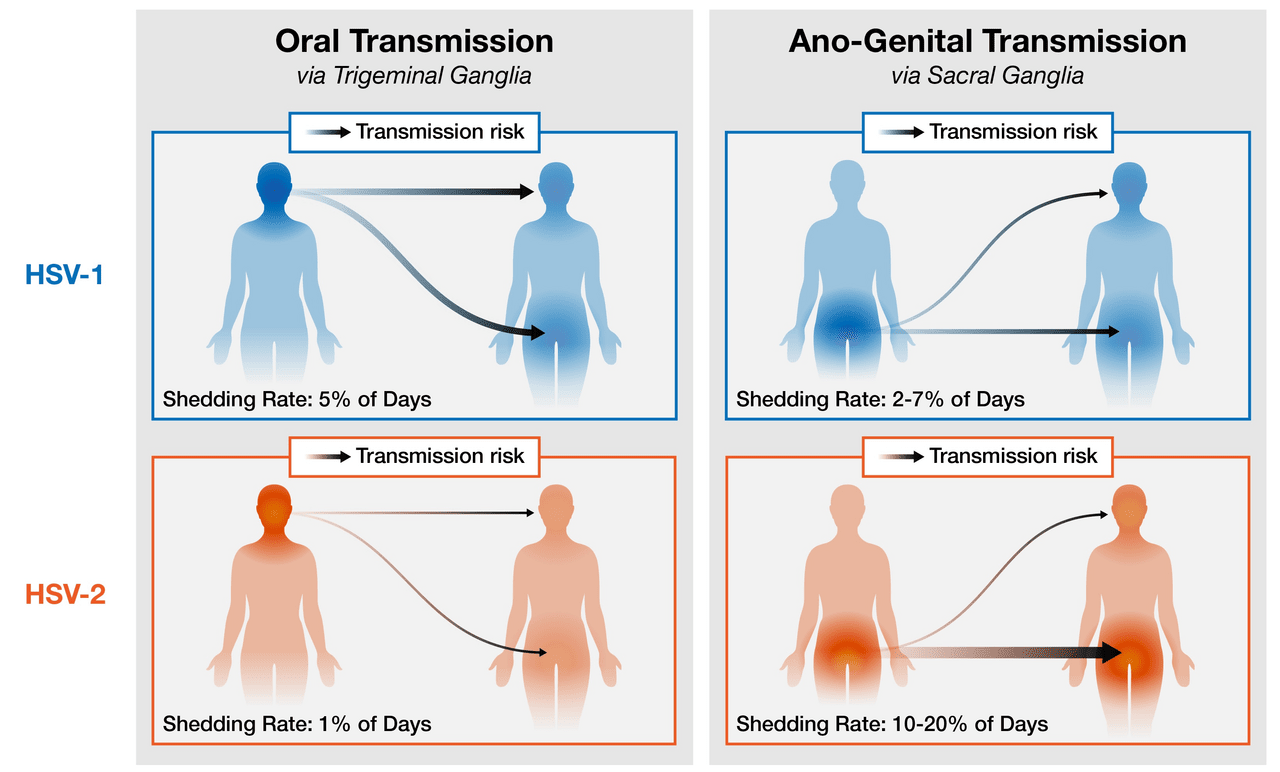
Sketch showing both HSV1 and HSV2 can spread through oral or genital contact.
However, HSV2 spreads more commonly with genital contact.
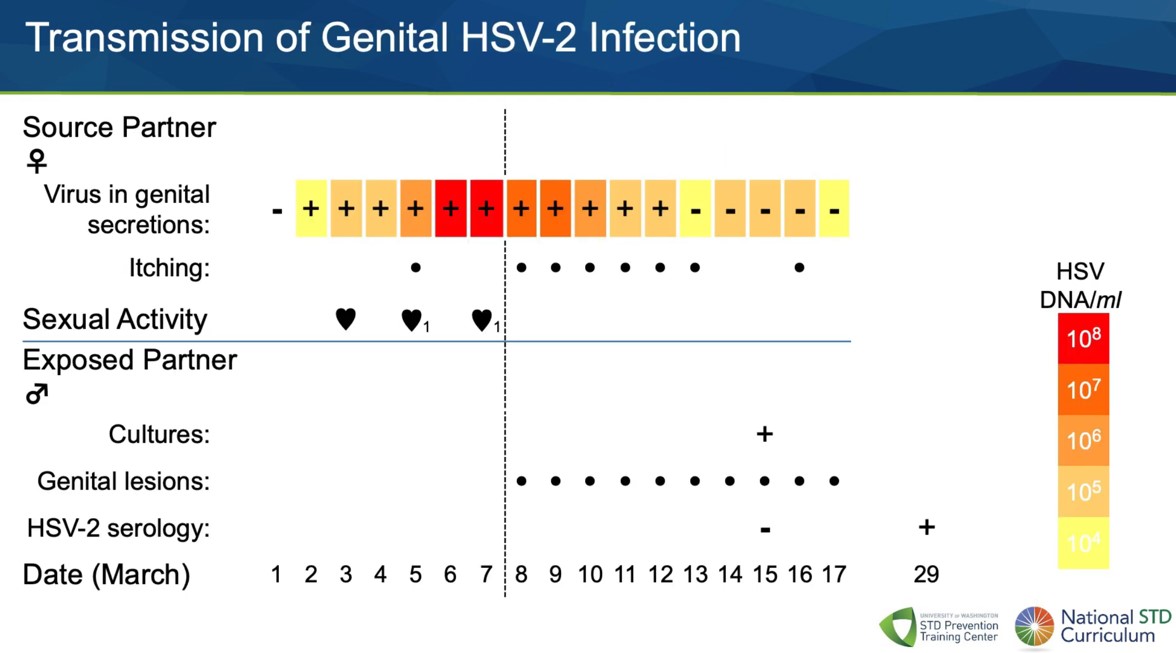
This real life case shows how a partner was infected through sexual contact over two weeks: genital rashes appeared within a week (day 8) of first sexual contact (on days 3, 5 7), and the virus could be detected within two weeks with a cultured swab sample (day 15). Source: std.uw.edu.
As per CDC, herpes has no cure, but flairs can be reduced with antivirals.
An antibody STD test can help in diagnosis and treatment if one suspects an infection.
Herpes outbreaks are very common when the virus shedding is highest.
Safe sex and a herpes STD test can help prevent the infection.

The STD Trichomoniasis or Trich is caused by a parasite trichomonas vaginalis.
After HPV and HSV, it is one of the most common STD in America.
You may have a Trich infection and may not know it. That's because Trichomoniasis symptoms are not always clearly visible. But a Trich STD test might be able to easily detect it.
Women are more commonly infected than men and are likely to show the symptoms.
Trich is easily treatable with antibiotics. But it's important to get tested first.
If you suspect a Trich STI for yourself or your partner, the CDC recommend to go to an STD testing clinic near you.
Or you can order one of the at-home STD test kits, which are as accurate and affordable.
They also offer the privacy and security one desires for such a personal matter.

The STI Bacterial Vaginosis is not fully understood yet.
However, women who will multiple partners or use a douche or have an IUD (intrauterine device) for birth control are at higher risk of BV infection.
Symptoms of BV are not clear, but you may see an unusual discharge, itching or fish-like smell from vaginal area. The symptoms of Bacterial Vaginosis often appear after having sex.
HIV is the most famous sexually transmitted virus. Human immunodeficiency Virus attacks the immune system, making it extremely difficult for our body to fight it.
If untreated, it can result into AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), which is a serious condition that has killed millions of people over past four decades.
Today, antiretroviral therapy and other medical breakthroughs have made it possible to live a normal healthy life. However, protected sex and PrEp (pre-exposure prophylaxis) can effectively avoid spread of HIV.
These are viral infections that can damage the liver. Besides sexual transmission, they can also spread via blood transfusion and sharing needles (e.g., during drug use).
They may not always show any symptoms but often appear as pain in the abdomen region, yellow eyes and skin, dark urine, and fatigue. Hepatitis B can be prevented with vaccination.
Mpox is a relatively new sexually transmitted disease that results in sores and lesions on the body.
This viral disease can spread through kissing, touching or sex, especially in men having relationships with other men.
A new vaccine is now available and it is easy to get tested for monkeypox.
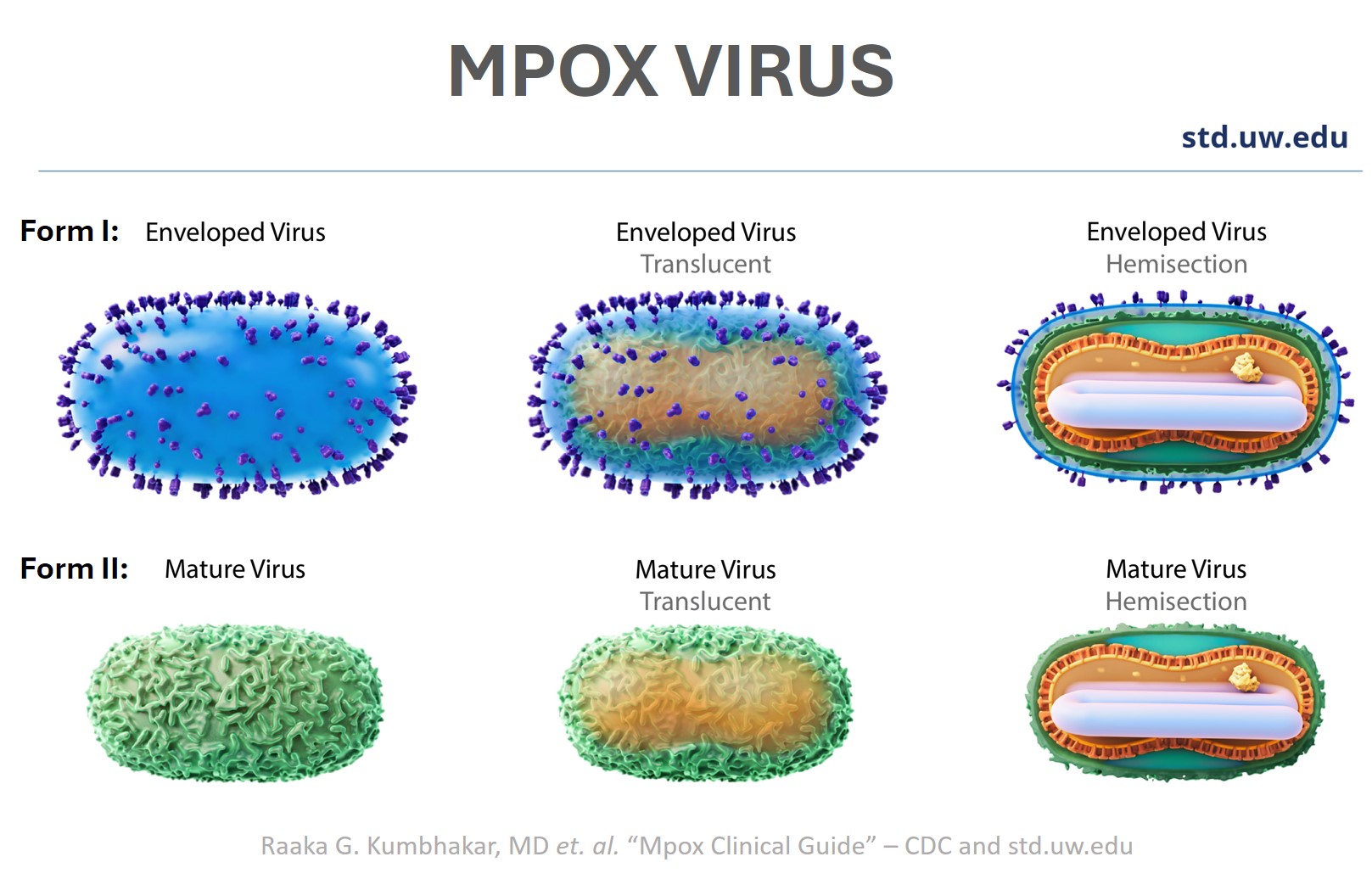
Mpox is caused by an ovoid, brick-shape virus from orthopoxvirus family. The monkeypox virus is really small: 0.2 microns with 19kb DNA.
Interestingly, the virus can exist in two distinct forms: outside the cells as enveloped (EV) & inside as mature virus (MV).
M. genitalium is one of the most difficult bacteria to detect.
Yet, it infected 3M US adults in 2017-18.
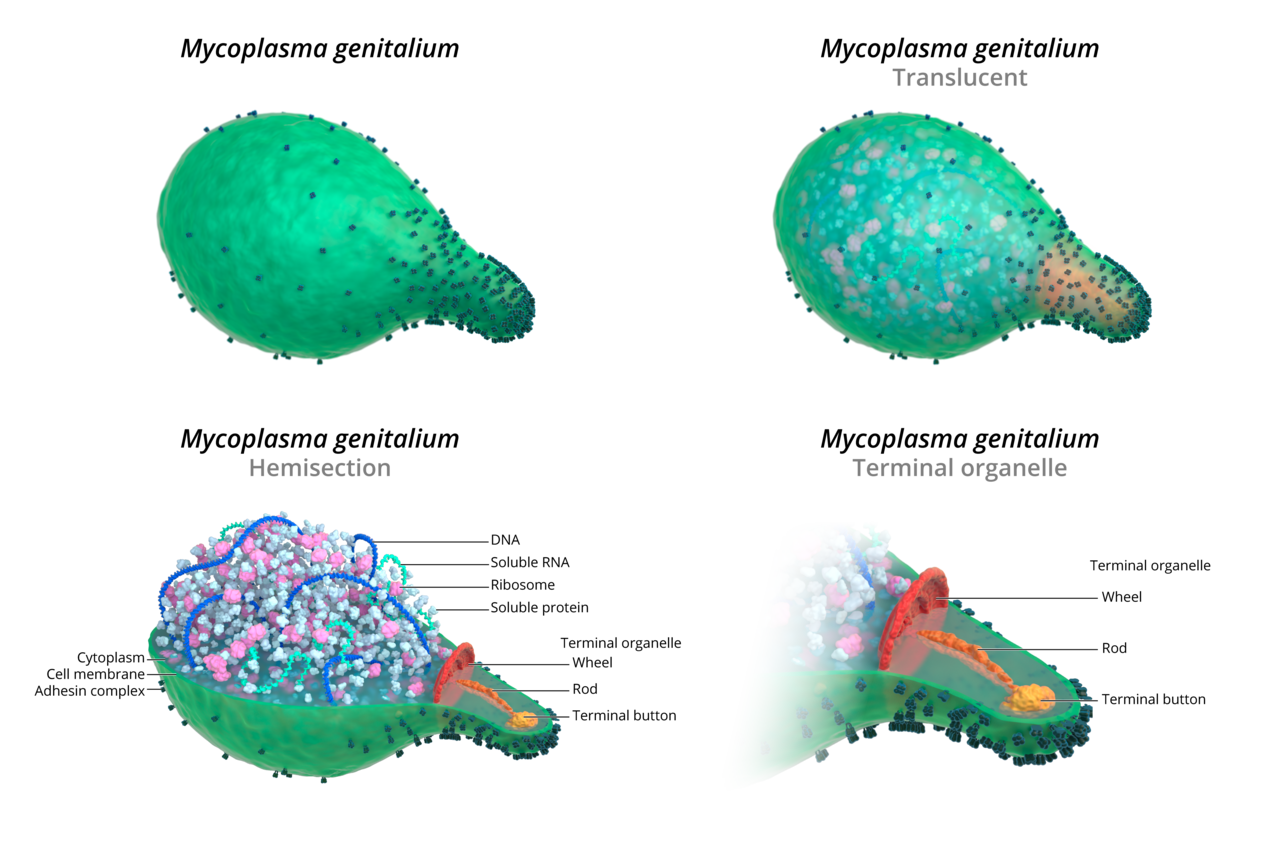
Sketch showing Mycoplasma genitalium. Reference: CDC, std.uw.edu; Image credit: Cognition Studio
Without a rigid wall, these flask shaped mobile & fastidious creatures are very difficult to grow in a lab and are rapidly becoming antibiotic-resistant.
They spread through sexual contact, causing range of issues e.g., pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) & fertility problems.

A short summary of 2022 data above from CDC say risk of different types of STDs to public health is growing.
STDs are huge burden on society due to the pain and suffering they cause. They consume public health resources that can be used elsewhere.
The stigma around STDs can prevent people from getting timely diagnosis and treatment. However, it is very easy to get tested for most of them.
An easy, simple swab or urine sample collected from the privacy of your home can help one get tested for STDs.
RxHomeTest offers multiple options to get tested and seek treatment as early as possible.

Order a Comprehensive STD Test kit.
Trichomoniasis - About Trich STD, Symptoms and Treatment - learn about the most common STD among women.
Chlamydia - STD Symptoms, At Home Testing and Treatment - know more about this easily treatable sexually transmitted disease.
Gonorrhea - STD Symptoms, Testing and Treatment - learn about the most common STD in teens and young adults.
The Most Challenging STD - Genital Herpes and HSV- learn about the most widespread STD across the world.
Hormone Imbalance in Women - Role of Estrogen, Progesterone and Testosterone - learn about key hormones for living a full life.
Hormone Testing - Role of FSH and LH Hormone Levels - how the two key hormones change with age.
Testosterone and Aging - an in-depth summary of science behind the male hormone.
Sexually Transmitted Infections Treatment Guidelines 2021, Recommendations and Reports, July 23, 2021, 70(4);1–187.
Sexually Transmitted Infections: Adopting a Sexual Health Paradigm, National Academies Report, Mar 2023.
About Trichomoniasis - a CDC guide.